| [1] Lukman AI,Gong B,Marjo CE,et al.Facile synthesis, stabilization, and anti-bacterial performace of discrete Ag enanoparticles using Medicago sativa seed exudates.J Colloid Interface Sci.2011;353(2):433-444.
[2] Zhang XL,Niu HY,Yan JP,et al.Immobilizing silver nanoparticles onto the surface ofmagnetic silica composite to prepare magnetic disinfectant with enhanced stability and antibacterial activity.Colloid SurfA.2011;375(1-3):186-192.
[3] Zhang B,Lin Y,Tang XN,et al.Mechanism of antibacterial activity of silver and praseodymium-loaded white carbon black.J Rare Earths.2010;28(1):442-445.
[4] 丁爱武,黄茂芳,丁丽,等.纳米TiO2/天然橡胶复合材料的抗菌性研究[J].热带作物学报,2010,31(2):309-313.
[5] Lu W,Chen M,Wu LM.One-step synthesis of organic–inorganic hybrid asymmetric dimer particles via.J Colloid Interface Sci.2008;328(1):98-99.
[6] Xu BS,Niu M,Wei L Q,et al.The structural analysis of biomacromolecule wool fiber with Ag-loading SiO2 nano-antibacterial agent by UV radiation. J Photochem Photobiol A.2007;188(1):98-105.
[7] Liao CJ,Yu P,Zhao JQ,et al.Preparation and characterization of NaY/PVDF hybrid ultrafiltration membranes containing silver ions as antibacterial materials. Desalination. 2011; 272(1-3):59-65.
[8] Zhu XY,Bai RB,Wee KH,et al.Membrane surfaces immobilized with ionic or reduced silver and their anti-biofouling performaces.J Membr Sci. 2010;363(1-2): 278-286.
[9] Pant B,Pant HR,Pandeya DR,et al.Characterization and antibacterial properties of Ag NPs loaded nylon-6 nanocomposite prepared by one-step electrospinning process. Colloids Surf A.2012;395(5):94-99.
[10] Rai M,Yadav A,Gade A.Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. BiotechnolAdv. 2009;27(1): 76-83.
[11] 曾戎,岳汉民,曾汉民.活性炭纤维对贵金属的吸附[J].材料研究学报,1998,12(2):203-206.
[12] 陈君华,王飞,丁志杰,等.银改性六方介孔硅的合成及其抗菌性能的研究[J].南京林业大学学报:自然科学版,2009,33(2):107-113.
[13] Akhavan O. Lasting antibacterial activities of Ag–TiO2/Ag/a-TiO2 nanocomposite thin film photocatalysts under solar light irradiation.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2009;336 (1):117-124.
[14] Thiel J,Pakstis L,Buzby S,et al.Antibacterial properties of silver-doped Titania.Small.2007;3(5):799-800.
[15] Holt KB,Bard AJ.Interaction of silver(I) ions with the respiratory chain of Escherichia coli: an electrochemical and scanning electrochemical microscopy study of the antimicrobial mechanism of micromolarAg+. Biochemistry. 2005;44(39):13214-13223.
[16] Lok CN,Ho CM,Chen R,et al.Proteomic analysis of the mode of antibacterial action of silver nanoparticles.J Proteome Res. 2006;5(4):916-924.
[17] Thomas V,Yallapu MM,Sreedhar B,et al.A versatile strategy to fabricate hydrogel-silver nanocomposites and investigation of their antimicrobial activity.J Colloid Interf Sci. 2007;315(1): 389-395.
[18] Nicolle LE.Catheter-related urinary tract infection.Drugs Aging. 2005;22(8):627-631.
[19] Plowman R,Graves N,EsquiVel J,et al.An economic model to assess the cost and benefits of the routine use of silver alloy coated urinary catheters to reduce the risk of urinary tract infections in catheterized patients.J Hosp lnfect. 2001;48(1): 33-42.
[20] 李秋明,付宜鸣,申景岭,等.人尿道黏膜上皮细胞的分离培养与鉴定[J].解剖科学进展,2008,14(4):406-408,412.
[21] 医疗器械生物学评价,第5部分,体外细胞毒性实验[S].GB/T 16886.5-2003.
[22] 范微微,吕伟,范巨峰.人正常泌尿系上皮细胞系作为组织工程化尿道种子细胞的可行性研究[J].中国美容医学, 2012,21(3): 433-435.
[23] 郝维平,姚友生,王家伟,等.人类膀胱移行上皮细胞的体外培养与鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(50):9348- 9352.
[24] 郝和平.医疗器械生物学评价标准实施指南[M].北京:中国标准出版社,2002.
[25] Maccallum DK,Lillie JH,Jepsen A,et al.The culture of oral epithelium.Int Rev Cytol.1987;109:313-330.
[26] 吴阶平.吴阶平泌尿外科学(上卷)[M].济南:山东科学技术出版社,2009:57.
[27] Li Q,Ionut I,Jeff L,et al.Numerical simulation of crack formation in all ceramic dental bridge.Key Eng Mater. 2006; 312:293-298.
[28] Kirkpatrick CJ,Bittinger F,Wagner M,et al.Current trends in biocompatibility testing.Proc Inst Mech Eng H.1998;212(2): 75-84.
[29] Lin WS,Huang YW,Zhou XD,et al.In vitrotoxicity of silica nanoparticles in human lung cancer cells.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.2006;217(3):252-259.
[30] Hussainin SM,Hess KL,Gearhart JM,et al.In vitro toxicity of nanoparticles in BRL 3A rat liver cells.Toxicol in Vitro. 2005; 19(7):975-983.
[31] Carlson C,Hussainin SM,Schrand AM,et al.Unique cellular interaction of silver nanoparticles:size-dependent generation of reactive oxygen species.J Physical Chem B.2008;112(43): 13608-13619.
[32] 张富强,余文珺,傅远飞.六种纳米载银无机抗菌剂的体外细胞毒性比较[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2005,40(6):504-507.
[33] Ke X,Jie XW,Xu LK,et al.Fabrication of antibacterial monodispersed Ag-SiO2 core-shell nanoparticles with high concentration.Mater Lett.2009;63:31-33.
[34] Wibberg D,Tielen P,Blom J,et al.Genome Sequence of the Acute Urethral Catheter Isolate Pseudomonas aeruginosa MH38.Genome Announc.2014;2(2).pii: e00161-14.
[35] Dhanalekshmi KI,Meena KS.Comparison of antibacterial activities of Ag@TiO<sub>2</sub> and Ag@SiO<sub>2</ sub> core-shell nanoparticles.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc.2014;128C:887-890.
[36] Dong M,Tian Y,Pappas D.Facile Functionalization of Ag@SiO<sub>2</sub> Core-Shell Metal Enhanced Fluorescence Nanoparticles for Cell Labeling.Anal Methods. 2014;6(5):1598-1602.
[37] Wang HS,Wang C,He YK,et al.Core-Shell Ag@SiO2 Nanoparticles Concentrated on a Micro/Nanofluidic Device for Surface Plasmon Resonance-Enhanced Fluorescent Detection of Highly Reactive Oxygen Species.Anal Chem. 2014;86(6):3013-3019. doi: 10.1021/ac4037075.
[38] Gangishetty MK,Lee KE,Scott RW,et al.Plasmonic Enhancement of Dye Sensitized Solar Cells in the Red-to-near-Infrared Region using Triangular Core-Shell Ag@SiO2 Nanoparticles.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013; 5(21):11044-11051.
[39] 刘春,边海龙,牛梅,等.纳米Ag-SiO2抗感染导尿管的体外抑菌性能检测分析[J].中国药物与临床,2009,9(8):777-778.
[40] 郭云童,刘春,张利.纳米Ag-SiO2导尿管在家兔导尿管相关性尿路感染中抗菌性的研究[J].山西医科大学学报,2010,7(41): 609-612.
[41] 翟军红,郭云童,刘春,等.纳米Ag-SiO2导尿管的细胞毒性评价[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(29):5371-5374. |
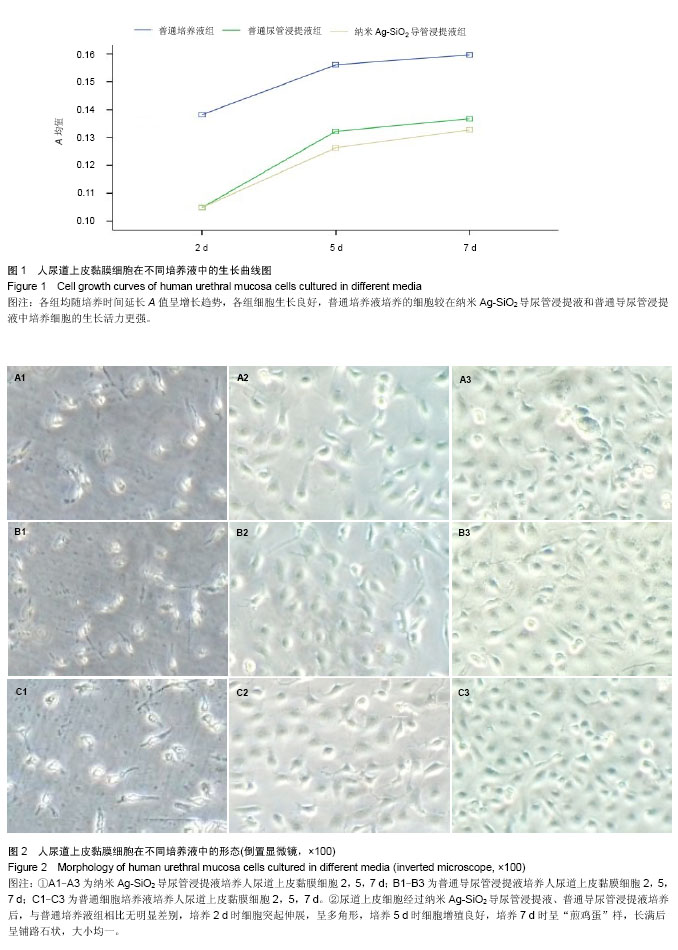
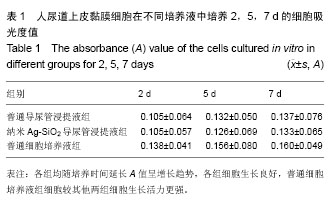
.jpg)